Neutron的VLAN实现模型
本文共 1906 字,大约阅读时间需要 6 分钟。
Neutron的VLAN实现模型如下图:
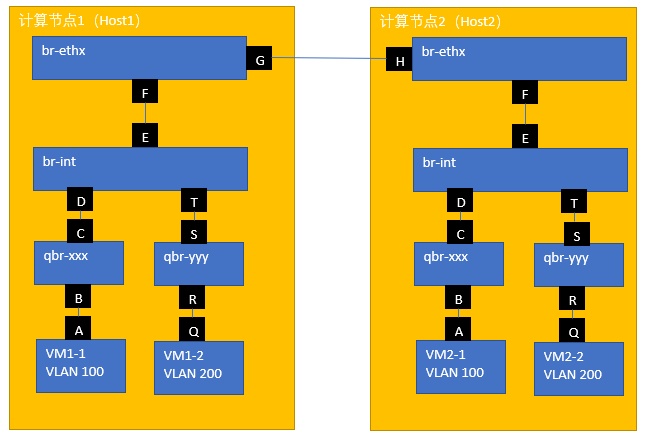
图中表达的是两个Host内的4个VM,分别属于两个VLAN:VM1-1与VM2-1属于VLAN 100,VM1-2与VM2-2属于VLAN 200。br-ethx、br-int、qbr-xxx、qbr-yyy都是Bridge,只不过实现方式不同。前两个选择的是OVS(Open vSwitch),后两者选择的是Linux Bridge。这些Bridge构建了两个VLAN(VLAN ID分别是100和200)。不同的Bridge之间、Bridge与VM之间通过不同的接口进行对接。
下面围绕这些内容,做一一介绍。
一 VM与VLAN ID
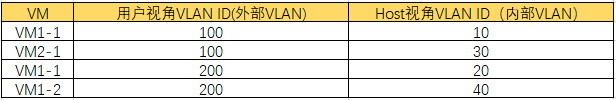
图中的4个VM组成了两个VLAN,VLAN ID分别是100和200.这两个VLAN ID有一定的说法,即有内外之别。我们先讲解内外之别是什么,后面再讲述为什么需要这个内外之别。
我们先看看下面这个简化的实现模型:忽略掉那些各种各样的Bridge,各种各样tap、veth pair等接口。简单理解,一个Host内有一个Bridge,Bridge连接着虚拟机。但是,图中的虚拟机的VLAN ID分别变成了10、20、30、40,与上面这个图中的100和200完全不是一个概念。这就涉及内外视角所看到的VLAN ID的不同。

外部视角是用户视角,它不关心内部实现细节,它只需要知道创建了两个VLAN网络,VLAN ID分别是100和200,每个VLAN里面有两个VM,如下图所示:

内部视角是在Host内部,4个VM的VLAN ID完全不是什么100、200,而是10、20、30、40、
内外视角的区别,见下表:
这里我们需要知道两点:
1 存在这样的内外之别。
2 这个内外之别需要做VLAN ID转换,而转换的功能,就是由Host内相应的Bridge来实现。
二 qbr及br-int
qbr-xxx、qbr-yyy一般简称qbr。qbr这个缩写比较有意思,它是Quantum Bridge的缩写,而Openstack网络组件的前一个商标名称就是Quantum,只不过由于版权的原因,才改为Neutron。从这个称呼我们也能看到Neutron里面Quantum的影子。
br-int,表达的是Integration Bridge(综合网桥)的含义。
qbr与br-int都是Bridge。qbr的实现载体是Linux Bridge,br-int的实现载体是OVS(Open vSwitch)。需要强调的是,并不是绝对地说qbr一定就是Linux Bridge,br-int一定就是OVS,也可以用其他的实现方式替换它们。只不过这样的实现方式是当前OpenStack解决方案的比较经典的方式而已。
qbr与br-int之间,通过veth pair连接,VM与qbr之间,通过tap连接。其实VM与qbr之间只有一个tap,也就是说1个tap分别挂载在VM和qbr之上。VM和qbr之间各画1个tap只是一种“艺术”的加工,以便于阅读和理解。
这里面有个问题:为什么需要两层Bridge?VM先接qbr(Linux Bridge),再接br-int(OVS),为什么不是VM直接接入br-int?原因有两个:
1 如果只有一个qbr,由于qbr仅仅是一个Linux Bridge,它的功能不能满足实际场景的需求。
2 如果只有一个br-int,由于br-int实际是一个OVS,而OVS比较任性,它到现在竟然还不支持基于iptables规则的安全组功能,而Openstack偏偏是要基于iptables规则来实现安全组功能。
所以Openstack引入qbr其目的主要就是利用iptables来实现security group功能(qbr有时候也被称为安全网桥),而引入br-int,才是真实为了实现一个综合网桥的功能。
三 br-ethx
br-ethx也是一个Bridge,也是一个OVS,它的含义是:Bridge-Ethernet-External。顾名思义,br-ethx负责与“外”部通信,这里的“外”部指的是Host外部,但是却又要属于一个network的内部。
br-ethx与br-int之间的接口是veth pair。
值得注意的是:br-ethx上的接口是一个真正的Host网卡接口。网卡接口是网卡物理口上的一个Interface。
四 内外VLAN ID的转换
前文提到内外视角的VLAN ID,在此直接讲述内外VLAN ID的转换过程。
1 出报文VLAN ID 转换过程
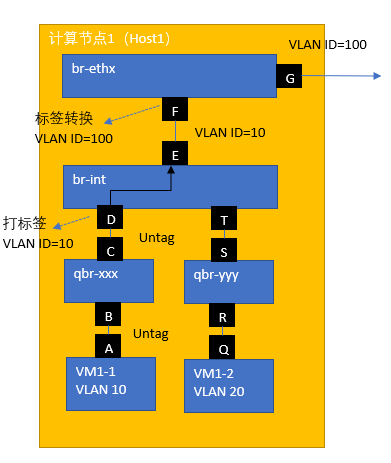
2 入报文VLAN ID转换过程

你可能感兴趣的文章